Raw Meat Diet for Dogs with Allergies: Is it the Right Choice?
Food allergies in dogs can manifest in various ways, from skin irritations and gastrointestinal upset to more severe reactions. Identifying and managing these allergies is crucial for ensuring your furry friend’s comfort and well-being. While traditional commercial dog foods often contain potential allergens, some pet owners are turning to alternative diets like the raw meat diet, also known as the BARF (Biologically Appropriate Raw Food) diet. This article explores the potential benefits and risks of raw meat diets for dogs with allergies, providing valuable insights for pet owners considering this dietary approach.
Understanding Dog Allergies
Before delving into the specifics of raw meat diets, it’s essential to understand the basics of dog allergies. Allergies occur when a dog’s immune system overreacts to a harmless substance, known as an allergen. Common allergens in dog food include:
- Beef
- Chicken
- Dairy
- Eggs
- Wheat
- Soy
- Corn
Symptoms of food allergies in dogs can vary widely and may include:
- Itching and scratching
- Skin rashes and inflammation
- Hair loss
- Ear infections
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Flatulence
Diagnosing food allergies in dogs can be challenging, as symptoms can mimic other conditions. Veterinarians typically use elimination diets to identify the culprit allergen. This involves feeding the dog a limited-ingredient diet with novel protein and carbohydrate sources, gradually reintroducing other ingredients to monitor for reactions.
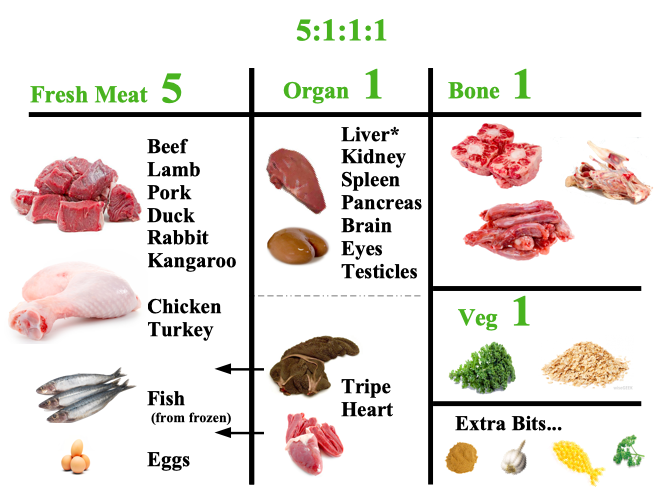
The Raw Meat Diet: An Overview
The raw meat diet is based on the premise that dogs are naturally designed to eat raw, unprocessed foods similar to what their wild ancestors consumed. A typical raw meat diet consists of:
- Raw muscle meat
- Raw bones (edible)
- Raw organ meat
- Raw vegetables and fruits
- Raw eggs
- Dairy (optional, e.g., yogurt, kefir)
- Supplements (e.g., omega-3 fatty acids, probiotics)
Proponents of raw meat diets argue that these diets offer several potential benefits for dogs, including:
- Improved digestion
- Increased energy levels
- Shinier coat
- Healthier teeth and gums
- Reduced allergy symptoms
Raw Meat Diet and Dog Allergies: Potential Benefits
For dogs with allergies, a raw meat diet may offer some advantages over traditional commercial dog foods.
Elimination of Common Allergens
Raw meat diets allow pet owners to control every ingredient their dog consumes. By carefully selecting novel protein and carbohydrate sources, it may be possible to avoid common allergens found in commercial dog foods, such as beef, chicken, wheat, soy, and corn.
Reduced Additives and Preservatives
Commercial dog foods often contain artificial additives, preservatives, and fillers that can trigger allergic reactions in sensitive dogs. Raw meat diets, on the other hand, are typically free from these potentially harmful ingredients.
Improved Digestibility
Raw meat is believed to be more easily digestible for dogs than processed kibble. The natural enzymes present in raw meat can aid in digestion, reducing the likelihood of gastrointestinal upset and allergic reactions.
Enhanced Nutrient Absorption
Raw meat diets are often rich in essential nutrients, such as protein, vitamins, and minerals. The nutrients in raw meat are also more bioavailable, meaning they are more easily absorbed and utilized by the body. This can help to support overall health and reduce allergy symptoms.
Raw Meat Diet and Dog Allergies: Potential Risks
While raw meat diets may offer some benefits for dogs with allergies, it’s essential to be aware of the potential risks associated with this dietary approach.
Bacterial Contamination
Raw meat can harbor harmful bacteria, such as Salmonella, E. coli, and Listeria. These bacteria can pose a health risk to both dogs and humans, especially those with weakened immune systems. Proper handling and storage of raw meat are crucial to minimize the risk of bacterial contamination.
Nutritional Imbalances
Raw meat diets can be nutritionally unbalanced if not formulated correctly. Dogs require a specific balance of protein, fat, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals to thrive. Feeding a raw meat diet without proper guidance from a veterinarian or veterinary nutritionist can lead to nutritional deficiencies or excesses.
Bone-Related Hazards
Raw bones can be a choking hazard for dogs, especially if they are small or brittle. Bones can also splinter and cause damage to the digestive tract. It’s essential to choose appropriate bone types and sizes for your dog and supervise them closely while they are chewing on bones.
Parasites
Raw meat can contain parasites, such as worms and protozoa. These parasites can cause gastrointestinal upset and other health problems in dogs. Freezing raw meat for several weeks can help to kill some parasites, but it’s not always effective.
How to Introduce a Raw Meat Diet to a Dog with Allergies
If you’re considering switching your dog with allergies to a raw meat diet, it’s essential to do so gradually and under the guidance of a veterinarian or veterinary nutritionist. Here are some tips for introducing a raw meat diet:
Consult with Your Veterinarian
Before making any dietary changes, it’s crucial to consult with your veterinarian. They can help you determine if a raw meat diet is appropriate for your dog’s specific needs and health condition.
Start Slowly
Introduce the raw meat diet gradually over several days or weeks. Begin by mixing a small amount of raw food with your dog’s current food, gradually increasing the proportion of raw food while decreasing the proportion of kibble.
Choose Novel Protein Sources
When introducing a raw meat diet for a dog with allergies, start with novel protein sources that your dog has never eaten before. Examples include rabbit, venison, duck, or fish.
Monitor for Reactions
Closely monitor your dog for any signs of allergic reactions, such as itching, skin rashes, vomiting, or diarrhea. If you notice any adverse reactions, discontinue the raw meat diet and consult with your veterinarian.
Ensure Proper Hygiene
Practice strict hygiene when handling raw meat to minimize the risk of bacterial contamination. Wash your hands thoroughly after handling raw meat, and disinfect all surfaces that have come into contact with raw meat.
Supplement as Needed
Work with your veterinarian or veterinary nutritionist to ensure that your dog is receiving all the essential nutrients they need. You may need to supplement the raw meat diet with vitamins, minerals, or other nutrients to ensure optimal health.
Conclusion
A raw meat diet can be a viable option for some dogs with allergies, but it’s not without its risks. Before switching your dog to a raw meat diet, it’s essential to consult with your veterinarian or veterinary nutritionist to ensure that it’s the right choice for your dog’s specific needs and health condition. If you decide to proceed with a raw meat diet, do so gradually and under professional guidance, and always prioritize proper hygiene and food safety practices.
This information is intended for educational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional veterinary advice. Always consult with your veterinarian before making any dietary changes for your dog.

